Vector's projection online calculator
Projection of the vector to the axis l is called the scalar, which equals to the length of the segment AlBl, and the point Al is the projection of point to the direction of the l axis, point Bl is the projection of the point to the direction of the l-axis:
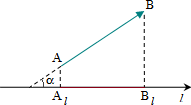
From the elementary geometrical considerations, it follows:
прl = AlBl = AB ∙ cos α = | | ∙ cos α
It's very easy to calculate the projection of the arbitrary vector to any decart axis, for instance, -axis. Here we have, cos α is the directional cosine of the vector :
Therefore, projection of the arbitrary vector on the decart axis, equals to corresponding coordinate of the vector.
A little bit complicated to calculate the projection of the abritrary vector to the arbitrary axis or arbitraty vector . In this case, we need to calculate the angle between corresponging vectors, what can be done by using the vectors scalar product formula:
, where φ - angle between vectors and .
Our online calculator is able to find the projection of one arbitrary vector to the another arbitraty vector with step by step solution.